If you have ever walked through a massive manufacturing hub in Baden-Württemberg or visited a chemical giant in the Ruhr region, you know that heat exchangers are the silent pulse of German industry. They are the workhorses keeping our breweries efficient, our district heating networks warm, and our automotive plants running at peak performance.
But let’s be honest: explaining the intricate internal geometry of a high-performance heat exchanger using only a 2D blueprint is like trying to describe the Nürburgring using only a list of street signs. It lacks the depth and energy of the real thing.
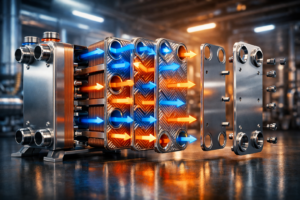
This is why Visualizing Heat Exchangers has become a game-changer. We are shifting away from flat, static drawings and moving into an era where CAD models are transformed into high-impact 3D animations. These visuals don’t just show a product; they demonstrate German engineering excellence in a way that anyone can understand.
Why the Shift to 3D Visualization?
In Germany, where “Vorsprung durch Technik” is a way of life, precision in heat-exchanger design is everything. However, the precision of data integration can be difficult to convey, especially when discussing the configuration and performance of heat exchangers across various case studies. If a client in Frankfurt or Munich can’t clearly see the turbulence in your flow channels, they might not appreciate the efficiency of your design. Visualizing these systems allows us to “open up” the steel and show the thermal dynamics in motion, highlighting the integration of heat exchanger design and the methodology used.
According to a 2024 report by Global Market Insights, the global heat exchanger market was valued at $17.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow significantly as industries prioritize energy optimization. To capture this growth, companies are turning to high-end visuals to prove their efficiency faster.
From Engineering Data to Visual Storytelling
Every great animation starts with the CAD model, which serves as the foundation for displaying heat exchanger dynamics and flow velocity. This is the precise “digital twin” created by the engineers. But a raw CAD file is built for the factory floor, not for a marketing presentation or a trade fair in Hannover. It is often too heavy to load quickly and lacks the “soul” of a finished product, especially when dealing with complex numerical data.
To create high-impact visuals, we take that engineering data and give it a “photo-real” finish, enhancing the design and analysis of heat exchangers. We apply textures that resemble genuine brushed stainless steel or titanium and set up lighting that makes the machine look like a piece of industrial art, showcasing its shell-side features. This transition from a rigid file to a fluid visual tool is what helps German firms stand out in a crowded global market.
Explore the benefits of 3D-printed heat exchangers and discover how they are transforming thermal system design. From improved heat transfer and optimized pressure drop to enhanced design flexibility, these innovative solutions open new possibilities for efficiency and performance in industrial and HVAC applications.
The Power of 3D Animation in Global Markets
Why are German businesses investing so heavily in these visuals? The data supports prediction and analysis of heat exchanger design, ensuring efficient heat transfer. According to optimization techniques, the efficiency of heat exchangers can be significantly improved by calibrating the objective function. Mordor Intelligence provides insights into the latest trends in heat-exchanger technology. The global 3D rendering and visualization market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% through 2026, driven by advancements in numerical simulations. German companies, known for their export strength, are using these tools to bridge the distance with international clients.
Furthermore, research in the heat exchanger industry highlights the importance of efficient thermal management and the impact of temperature differences on performance. Wyzowl shows that 88% of consumers say they’ve been convinced to buy a product after watching a video. In a technical field like thermodynamics, where the benefits are often hidden inside a metal box, a video isn’t just a luxury; it’s a vital sales tool for showcasing the heat exchange process.
Comparing Methods: 2D vs. 3D Visualization
| Feature the design of heat exchanger that maximizes thermal efficiency and minimizes fouling. | 2D Technical Drawings can sometimes fail to convey the intricate details of the heat exchanger configuration, particularly in terms of uniform and non-uniform flow characteristics. | 3D High-Impact Animations |
| Clarity in presenting the integration of various components in heat exchanger design is essential for effective communication and calibration of performance metrics. | Low; requires specialized engineering knowledge | High; intuitive for both CEOs and technicians |
| Engagement with advanced heat-exchanger designs can lead to better understanding and innovation in the field. | Static; easy to overlook during pitches | Dynamic; captures attention at trade shows with innovative heat exchanger designs. |
| Error Detection | Hard to visualize flow bottlenecks | Immediate visual feedback on fluid dynamics using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) results. |
| Marketing Value in the context of air conditioning systems is crucial for attracting customers. | Strictly functional | Highly shareable on LinkedIn and websites |
Making the Invisible Visible: Heat and Flow
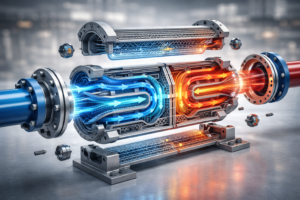
The real “wow” factor of Visualizing Heat Exchangers is its ability to provide a deeper understanding of the system’s overall heat transfer and pressure drop. It is the ability to see details that the human eye cannot, especially in complex systems such as two-phase heat exchangers with different flow configurations. We cannot visualize heat transfer directly, but in a 3D animation, we can use color gradients to show the heat transfer coefficient along the tube. We can show the “Hot Side” fluid entering as a vibrant red and gradually cooling to a deep blue as it transfers its energy through the plates.
For a maintenance team in a Berlin power plant, seeing an animation of how a specific valve opens or how a cleaning-in-place (CIP) system works is far more effective than reading a thick German-language manual. It simplifies training and prevents costly downtime, especially when addressing calibration issues.
See how 3D product visualization helps your business explore the benefits and practical applications of heat exchangers, making complex designs easy to understand and evaluate.
Tips for Creating High-Impact Visuals
If you are considering a 3D model for your thermal equipment, here are a few expert tips to optimize flow and temperature differences.
-
Highlight the Innovation: If your baffle design is unique, ensure the animation zooms in on that feature to analyze its impact on pressure drop and fluid distribution.
-
Simulate real-world conditions to analyze the velocity and performance of heat exchangers, with a focus on the exchanger inlet, boundary conditions, and constraints. Use physics-based particles to visualize fluid flow patterns through the heat exchanger inlet and outlet, illustrating flow velocity. It adds a level of realism that builds trust among other engineers in optimizing heat exchanger designs through discrete simulations.
-
Keep it Concise: A 60-second high-impact clip is often more effective than a 10-minute deep dive.
-
Use Cross-Sections: Use “clipping planes” to cut through the shell in real time, allowing the viewer to see the internal tubes and gaskets and enhancing the display of the heat transfer process.
Why German Industry is Leading the Way
Germany has long been at the forefront of the “Mittelstand”—highly specialized, world-leading companies in heat exchanger performance. To maintain this lead, these companies are adopting “Industry 4.0” visuals and exploring case studies on innovative methodologies. Whether you are selling a heat recovery system to a factory in Asia or presenting a new design to a board of directors in Hamburg, a 3D animation lets you bring the factory’s heat exchanger design and its life-cycle benefits to life.
Investing in these visuals is a strategic choice to highlight the integral role of heat exchangers in modern engineering. It allows your sales team to demonstrate a 20-ton industrial unit on a simple tablet or through a VR headset, making the complex simple and the invisible visible.
Want to boost your brand by showcasing your innovative heat exchanger designs and their optimization through advanced computational fluid dynamics? Discover why businesses should invest in 3D animation for marketing and how it can transform your market presence.
Wrapping Up: The Future is Visual
As the world moves toward greener energy and more efficient thermal management, the ability to communicate your “green” credentials and the overall heat performance of heat exchangers is key. By Visualizing Heat Exchangers through professional 3D animations, you show that your company isn’t just following the future—you are building it with a wide variety of heat exchanger solutions.
Whether it is for the automotive sector, renewable energy, or food production, remember: an engineering drawing shows how it’s built, but an animation shows how it manages mass flow rate and temperature differences.
Is your engineering team ready to transform complex schematics into a powerful sales engine? Explore how our Industrial and Engineering 3D Animation services can bring your technical innovations to life.
FAQs: Visualizing Heat Exchangers
What are the 4 types of heat exchange?
The four primary types of heat exchangers are: single-phase, two-phase, air-cooled, and liquid-cooled configurations.
-
Double Pipe: A simple design where one pipe is nested inside another, often used in chemical processes for efficient heat transfer.
-
Shell and Tube: a geometric design commonly used in heat exchangers. A very common industrial design featuring a bundle of tubes inside a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, optimized for the heat exchange process and constrained by geometric factors.
-
Plate Heat Exchanger: an integral component for efficient heat transfer in various applications, particularly in convection processes. Uses a series of metal plates in a shell-and-tube heat exchanger to transfer heat between two fluids, optimizing the amount of heat transferred.
-
Adiabatic Wheel technology is revolutionizing the design and analysis of energy-efficient systems. Uses a rotating wheel to transfer heat between two air streams.
How does a heat exchanger work?
A heat exchanger work video typically uses 3D animation to show two fluids of different temperatures flowing through separate channels, illustrating the principles of heat and mass transfer. The video illustrates how heat is transferred through the dividing wall (plate or tube) without the fluids mixing, using color-coded “thermal” visuals to show temperature changes during the heat-exchange process.
What is the dynamic model of a heat exchanger?
A dynamic model is a digital simulation that shows how the system changes over time, often utilizing an algorithm to predict outcomes. Unlike a “static” model, it accounts for variables such as startup and shutdown, and how it responds when fluid flow is suddenly increased or decreased, affecting both mass flow rate and heat transfer.
What are the real-life applications of heat exchangers?
Heat exchangers are used across almost every industry in Germany, including:
-
Automotive: Radiators and oil coolers in vehicles.
-
Energy efficiency is crucial in the performance of heat exchangers. Boilers and condensers in power plants are essential components that integrate with heat exchangers to enable efficient thermal management.
-
HVAC systems play a crucial role in the overall heating and cooling of residential and commercial buildings. Heating and cooling systems for homes and offices are critical in maintaining optimal flow rate and energy efficiency.
-
Manufacturing: Cooling down machinery and pasteurizing products in food processing.