Heat exchangers equipped with advanced technology are everywhere, playing a crucial role in efficient heat dissipation. They keep our cars cool, help heat our homes, and play a key role in industrial processes, particularly with bespoke heat exchangers. In recent years, engineers have begun using 3D printing, which has experienced rapid growth, to develop advanced heat-transfer applications that improve heat-exchange efficiency. The goal is to create new heat exchangers that outperform traditional designs, particularly in heat-transfer performance.
In this article, we will explore the thermal management applications of 3D printing technologies and the range of 3D-printed heat exchangers. The advantages of 3D‑printed heat exchangers include enhanced thermal efficiency in a compact form factor, design freedom, and the ability to create highly optimized heat sinks tailored for heat dissipation. This approach offers significant benefits over conventional ones, particularly when enhanced by 3D design software.
The global heat exchanger market is growing rapidly, with the industry expected to expand from USD 20.25 billion in 2023 to nearly USD 36 billion by 2031, driven by advances in sustainable 3D printing for heat transfer. Meanwhile, the 3D-printed heat exchanger segment alone was valued at approximately USD 0.45 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at roughly 10 percent annually through 2034, driven by demand for heat exchangers.
Let’s look at why engineers increasingly see advantages of 3D‑printed heat exchangers tailored for real-world use, particularly in the optimization of 3D printed designs for efficiency using Tinkercad 3D design software 101.
Why 3D Printing Matters in Heat Exchangers
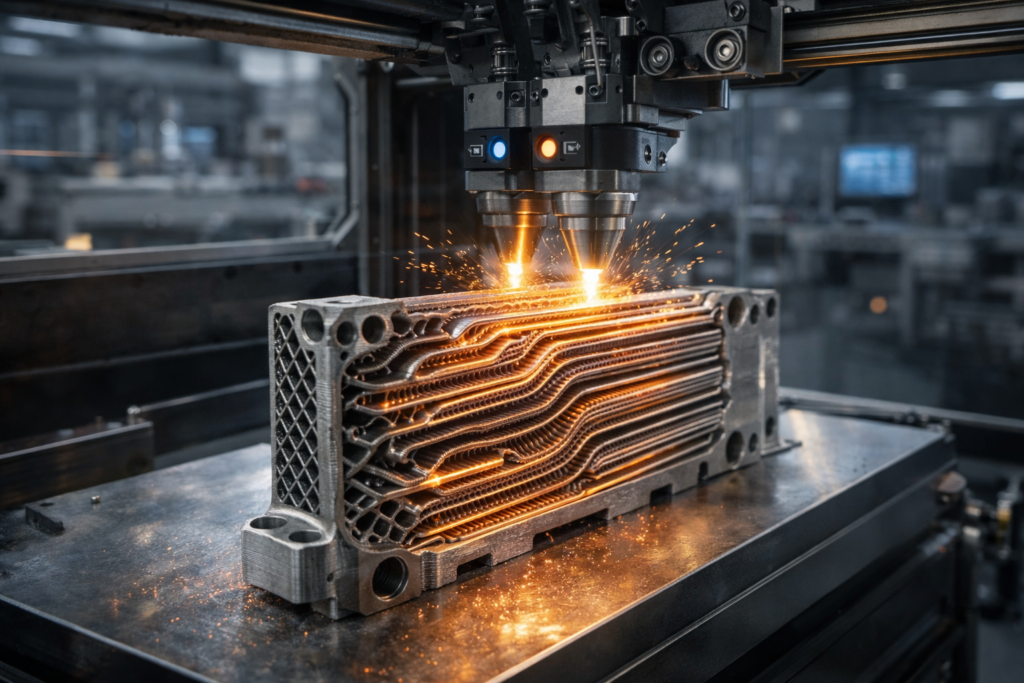
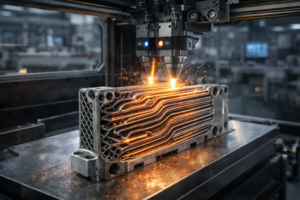
Traditional heat exchangers are often fabricated by welding or brazing tubes, plates, and fins, which limits overall heat-transfer efficiency and prevents them from meeting high-performance standards. These methods work well, but they limit the complexity of the internal channels in 3D-printed heat exchangers. 3D printing enables the creation of shapes once considered impossible, maximizing performance and customizing each component for specific heat-transfer applications, especially with optimized 3D-printed materials for heat transfer.
If you want to visualize these advanced designs for clients or engineering teams, 3D printing enables innovative solutions that optimize heat transfer across a range of applications for 3D printed heat exchangers. Technical 3D animation for engineering can effectively demonstrate the benefits of 3D-printed heat exchangers. Complex geometries created through 3D printing can make heat transfer and thermal stress easier to visualize, especially when discussing the advantages of mini-channel heat sinks in 3D design.
Key Advantages of 3D‑Printed Heat Exchangers
Complex Geometries for Better Heat Transfer
3D printing enables designers to fabricate intricate internal pathways, such as microchannels, lattice structures, and optimized fins, thereby significantly increasing surface area for heat transfer. This increase in surface area can significantly improve thermal performance compared with conventional designs with simple straight channels, particularly in compact heat exchangers.
Research shows heat-transfer improvements of 15-50% in advanced 3D‑printed designs compared with conventional finned heat exchangers, highlighting the benefits of additive manufacturing. These complex pathways also help engineers control fluid flow to reduce resistance and enhance efficiency, thereby maximizing overall heat-transfer coefficients in heat exchangers tailored to various applications.
Part Consolidation and Leak‑Free Designs
Traditional heat exchangers require multiple parts joined by welding or brazing, whereas additive manufacturing enables more integrated designs. These joints are potential leakage points and often require careful inspection and maintenance.
3D‑printed heat exchangers can be manufactured as a single monolithic part. Using 3D design software enables designs with no assemblies, producing heat exchangers fabricated via 3D printing that eliminate many leak points and reduce the risk of failure in thermal management systems. This improves reliability and often lowers maintenance costs, thereby enhancing heat transfer.
Lightweight and Compact Components
Because 3D printing adds material only where it is structurally and thermally needed, these heat exchangers can be much lighter and smaller, allowing for more efficient designs that meet maximum heat transfer capabilities. One industry example showed weight reductions of up to 85 percent and size reductions to one‑fifth of the original traditional part, enhancing the potential of 3D printing in heat exchanger applications.
This is particularly useful in aerospace and automotive applications in Germany, where the efficient heat exchangers produced by 3D printing are crucial for high-heat applications. To showcase these lightweight designs to clients or investors, adopting 3D printing technology and 3D design software with a 101-level interface is essential.
3D technical animation for infrastructure in Germany showcases the benefits of 3D printing in enhancing heat-transfer applications, particularly through the use of efficient heat exchangers tailored to diverse needs. These complex pathways illustrate how heat exchangers enable efficient heat transfer.
Rapid Prototyping and Development
In conventional manufacturing, creating a prototype can take weeks or months due to tooling and complex fabrication processes, whereas 3D printing has seen significant advances that can shorten this timeline. With 3D printing, designers can go from digital design to a physical part in days or weeks, accelerating testing and iteration.
This allows engineers to refine designs faster using 3D design software, improving performance while reducing development time and cost through the adoption of 3D printing.
Material and Energy Savings
Additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer, only where needed, optimizing thermal conductivity and enhancing heat transfer compared to subtractive methods. This reduces waste and lowers energy use, which can improve heat transfer compared to conventional processes.
For presentations or marketing to stakeholders, Photorealistic 3D rendering can be used to visualize compact heat exchanger designs that maximize convective heat transfer, enhancing the capabilities of 3D design software for heat treatment applications.
Customised Solutions
Every application is different, and 3D printing makes it easy to customise heat exchanger geometry for specific requirements, enhancing the optimization of 3D printed designs. Whether it’s high‑performance cooling for EV batteries, compact designs for aerospace, or tailored solutions for industrial HVAC systems, 3D printing delivers bespoke performance without prohibitive cost increases.
Table: Comparison of Traditional vs 3D‑Printed Heat Exchangers
| Feature | Traditional Heat Exchanger | 3D‑Printed Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Limited by fabrication methods, traditional heat exchangers often do not leverage the advantages of 3D printed heat exchangers across various applications. | Highly complex shapes possible with 3D printing techniques enhance the performance of heat exchangers. |
| Assembly | Multiple parts with joints | Single-part, no-joint heat exchangers are a notable advantage of heat exchangers made with 3D printing techniques. |
| Surface Area is a critical factor in the design of efficient heat exchangers tailored for optimal performance. | Standard fins or tubes can be used to visualize compact heat exchanger designs that maximize the surface area available for heat transfer. | Microchannels and custom flow paths are essential features in the design of efficient heat exchangers tailored for specific applications. |
| Weight | Heavier components can negatively impact heat dissipation in heat exchangers. | Often significantly lighter |
| Prototyping speed is essential in developing a polymer heat exchanger that maximizes heat transfer across the heat. | The slow adoption of 3D printing technology, known as 3D printing, can hinder advancements in heat exchanger design, which are crucial for improving flow, heat transfer, and thermal efficiency. | Rapid design testing is significantly enhanced by the capabilities of 3D printing technologies for heat exchangers, particularly those utilizing lattice heat structures. |
| Material waste is significantly reduced through the use of 3D printing in the production of heat exchangers. | High | Low material waste is a key benefit of using additive manufacturing for heat exchangers. |
| Customisation in 3D printing allows for the creation of efficient heat exchangers tailored to specific applications. | Costly technologies, such as traditional manufacturing, often cannot match the benefits of 3D printing. | Easy to customise |
| Leak Points | Many heat exchangers meet the demands of various industrial applications. | Reduced risk of leaks |
Practical Tip for Engineers
When considering 3D‑printed heat exchangers for industrial use, focus on applications that benefit from excellent thermal conductivity. Compact size or high surface area available for heat transfer are critical factors in the design of efficient heat exchangers.
These features are essential in electric vehicle battery cooling or aerospace thermal systems, where effective heat transfer within components is critical due to the high heat generated, particularly in the optimization of 3D printed heat exchangers. Partnering with an experienced additive manufacturing provider early in the design process helps optimize heat transfer in heat exchangers using complex geometries and maximize the surface area available for heat transfer.
Common Misconceptions
Some people think 3D printing is only good for prototypes, but the potential of 3D printing extends to advanced heat transfer applications, particularly in flow and heat transfer systems. In fact, additive manufacturing has experienced intense growth and is increasingly used for production, particularly in sectors where performance and weight matter more than unit cost, such as aerospace and high-end automotive applications for 3D printed heat exchangers.
Another misconception is that 3D‑printed components are always more expensive. While printers and materials for 3D printing can be costly upfront, the overall benefits in performance, material savings, and reduced assembly often outweigh those costs.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Heat Exchangers
The advantages of 3D-printed heat exchangers equipped with complex geometries go beyond novelty, particularly in their application for waste heat recovery and the use of materials for 3D printing. These components deliver performance improvements, reduce weight, save material, and unlock design possibilities that traditional manufacturing cannot match, particularly with ceramic heat exchangers designed for turbulent flow heat transfer.
As the 3D printing industry continues to grow and new additive technologies mature, the benefits of 3D printing in the heat exchanger sector will increase even further, especially in waste heat recovery. For engineers and manufacturers in Germany looking to push the boundaries of heat exchanger design and efficiency, 3D printing is a compelling tool that deserves serious consideration, especially in the context of waste heat recovery.
FAQs: Advantages of 3D-Printed Heat Exchangers
What are the advantages of 3D printing over traditional manufacturing?
3D printing allows for complex shapes, rapid prototyping, material savings, and customisation that traditional manufacturing cannot easily achieve, especially in applications for 3D printed heat exchangers.
What is the primary advantage of 3D printing over traditional methods for these irons?
The main advantage is the ability to create intricate, optimised geometries that improve performance without the need for assembly or multiple parts, especially in high-performance heat exchangers tailored through 3D printing.
What are some advantages of using a 3D printed mold compared to traditional molds?
3D printed molds can be produced faster, customised easily, and with less material waste than traditional mold-making processes, particularly with advanced 3D printing materials that help to optimize heat transfer.
What is a key advantage of metal 3D printing over traditional CNC machining?
A key advantage is that additive manufacturing can create internal channels and complex structures that enhance heat transfer in heat exchangers, which CNC machining cannot easily produce, thus revolutionizing heat transfer.