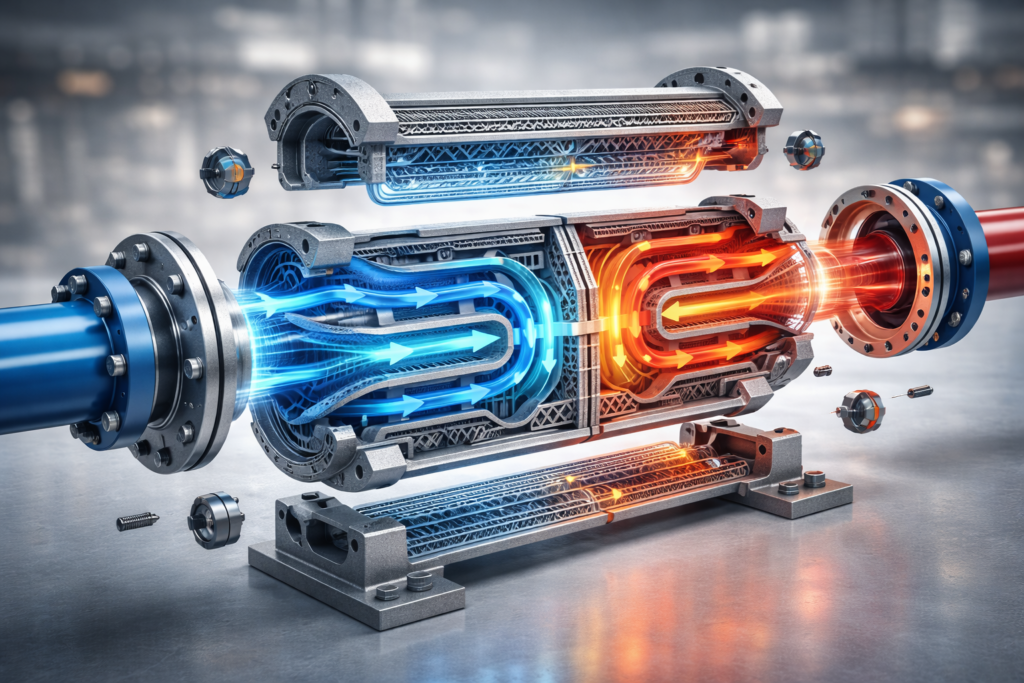
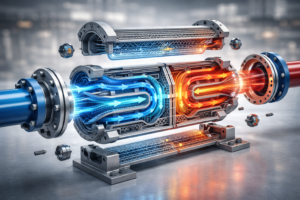
In the world of high-stakes engineering, heat exchangers have always been the unsung heroes. From the radiator in your car to the massive cooling systems in power plants, they keep the wheels of industry turning without a literal meltdown, ensuring efficient heat management.
But things are changing fast, especially with the introduction of innovative heat exchanger designs in industries such as aerospace.
The arrival of 3D printing has completely flipped the script on how we design these components. However, there is a catch. As we move toward complex, high-performance additively manufactured heat exchangers, new heat innovations will continue to emerge, expanding the design possibilities. Additive manufacturing of heat exchangers can significantly improve thermal efficiency and reduce pressure drop. We are finding that traditional 2D blueprints are no longer adequate, especially in the context of high thermal performance.
We need to see these designs in three dimensions to understand them, especially when evaluating high-performance heat exchangers truly.
The New Frontier of Cooling: Additive Manufacturing Heat Exchangers
Traditionally, building a heat exchanger was a bit like playing with Meccano, but now it can be achieved through advanced manufacturing methods that utilize conflux technology. You took tubes, fins, and plates, and you welded or brazed them together, but now you can use AM to create more efficient designs. It worked, but it was clunky compared to the latest heat exchangers still on the market. Additive manufacturing (AM) is used to develop compact heat exchangers.
Rather than being limited by the capabilities of a drill or a lathe, AM enables engineers to “grow” a heat exchanger layer by layer. This means we can create organic, wiggly, and highly efficient shapes that resemble something grown on a coral reef rather than something manufactured in a factory, thereby enhancing overall heat-transfer efficiency. These are often referred to as TPMS (Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces), used in the design of efficient heat exchangers with complex geometries.
While this sounds like science fiction, it’s very much a reality. But here’s the rub: if you can’t visualise these internal “nooks and crannies,” how can you be sure they’ll work? This is where 3D visualisation steps in to save the day, particularly in the design and manufacture of complex components.
Quick Thought: Within the broader context of modern industry, the design freedom offered by additive manufacturing is changing how heat exchangers are produced, while 3D animation is becoming essential for visualising automation and robotic systems.
Why 2D Drawings Are Simply Not Enough
Historically, a 2D technical drawing was the gold standard for designing heat exchangers. A couple of cross-sections and some dimensions were usually enough to get the job done, but now we rely on CFD to optimize designs. However, additive manufacturing heat exchangers can achieve remarkable heat-rejection capabilities that surpass conventional manufacturing methods, particularly in cold-plate applications, where heat exchangers enabled by this technology excel.
These heat exchangers are highly efficient and different from traditional designs. Their internal geometries are often so complex that a 2D slice doesn’t capture the full picture of maximizing heat-transfer performance in additively manufactured metal structures.
Imagine trying to explain the shape of a spiral staircase using only a photograph of one step, much like explaining heat transfer in heat exchangers may be complex without visual aids. You’d get the gist, but you wouldn’t understand the flow of the additively manufactured heat exchanger design. 3D visualisation allows engineers to “walk through” the device before a single grain of metal powder is lasered into place.
The Benefits of Seeing the Big Picture
-
Spotting design flaws in heat exchangers still requires careful analysis and testing. You can see where powder might become trapped during the additive manufacturing process for developing efficient heat exchangers.
-
Fluid Flow Analysis: Visualising how air or liquid flows through the device helps prevent “dead zones” where heat may accumulate.1
-
Stakeholder Buy-in: It is much easier to convince a manager to invest in a new design when they can see a stunning 3D render rather than a confusing line drawing.
The Power of Technical Clarity
When we talk about 3D visualisation, we aren’t just talking about pretty pictures. We are discussing “digital twins,” which can simulate the performance of heat exchangers under various pressure-drop conditions, enabling optimized additive-manufactured heat exchanger designs. These are exact virtual replicas of the physical part, created using advanced manufacturing techniques such as powder bed fusion.
For Additive manufacturing heat exchangers can greatly benefit from innovative design iterations and the use of cold plates., this is crucial because the surface area to volume ratio is so high.2 A tiny error in the digital file can lead to a massive failure in the physical part, especially in the context of high thermal applications in compact heat exchangers, where maximizing heat transfer is critical. By using advanced 3D rendering and animation, teams can simulate the thermal stresses the part will face in the real world.
If you’re wondering why this level of detail is becoming the industry standard in manufacturing, explore how additively manufactured components are used in aerospace applications and why technical 3D visualisation is essential for modern manufacturing and engineering.
Let’s Talk Numbers: The Impact of AM
To understand why everyone is making such a fuss about this, we have to look at the performance gains of additively manufactured heat exchangers, which often utilize advanced alloy compositions for high-temperature applications. Additive manufacturing isn’t just a “different” way to make things; it is often a “better” way.
-
Massive surface-area increases in complex-geometry heat exchangers make them more efficient. According to research published by leading experts in heat-exchange technology, significant advances are being made in heat-exchanger efficiency. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) is a key organization in advancing the standards for highly efficient heat exchangers. Additive manufacturing can increase a component’s heat-transfer surface area by reducing weight and improving efficiency. A 300% increase in efficiency is achievable with advanced heat exchangers enabled by innovative designs. Compared with traditional shell-and-tube designs, heat exchangers fabricated via additive manufacturing offer significant advantages.
-
Weight Reduction: Utilizing additive manufacturing can significantly reduce weight in designs while improving the efficiency of heat exchanger production. High-authority reports from GE Additive Research indicate that 3D-printed heat exchangers produced via additive manufacturing can achieve nearly 50% weight savings, reducing costs. This represents a 50% reduction in weight for the new high-efficiency heat exchangers, which is vital for aerospace applications. while maintaining (or even exceeding) the thermal performance of their heavier, traditional counterparts thanks to advanced powder bed fusion techniques.
Comparing Traditional vs. Additive Heat Exchangers
| Feature: The use of metal powder bed fusion technology enables intricate designs that were previously impossible to achieve in additively manufactured heat exchangers. | Traditional manufacturing methods are being supplanted by additive manufacturing processes for producing heat exchangers with complex geometries. | Additive Manufacturing |
| Design freedom in additive manufacturing enables the fabrication of intricate geometries that enhance thermal conductivity in heat exchangers, particularly when employing additive manufacturing to fabricate complex designs. | Limited by machining tools, industries such as aerospace are exploring new design possibilities. | A wide range of organic shapes can be achieved using additive manufacturing to design complex heat exchangers. |
| Internal complexity in heat exchangers enabled by additive manufacturing can lead to better performance and efficiency. | Simple tubes and fins can be enhanced through metal 3D printing to improve thermal conductivity. | Complex lattices and TPMS are revolutionizing the design of heat exchangers in aerospace applications through additive manufacturing. |
| Weight | Often heavy due to joints/plates, traditional designs are evolving with the advent of additive manufacturing technologies. | Highly optimised and lightweight designs are crucial for effective heat exchange in additive manufacturing processes, particularly in high-performance heat exchangers. |
| Assembly of high-performance heat exchangers requires precision to ensure optimal performance. | Requires welding/brazing | Printed as a single monolithic part |
| Visualisation Need: To fully leverage advanced manufacturing, we need to visualize the design features of the heat exchangers. | Moderate (2D is usually fine) designs are often insufficient for the complex requirements of heat exchange in additive manufacturing, especially when developing highly efficient heat exchangers. | Critical (3D is essential in the manufacturing process) |
Making the Invisible Visible
One of the most valuable aspects of using 3D visualisation for designing efficient heat exchangers is the ability to optimize the performance of additive-manufactured heat exchangers. The ability to visualize “invisible” processes is crucial for understanding efficient heat transfer in 3D-printed heat exchangers. You can’t see heat moving with the naked eye, and you certainly can’t see how fluid turbulates inside a sealed metal block, which is critical for understanding heat exchangers still in development for improved efficiency.
With 3D animation, you can peel back the outer layers of the novel heat exchanger and watch the thermal exchange happen in real-time. This is a transformative development for marketing and sales in the realm of high-performance heat exchangers enabled by advanced technology. If you can show a client exactly how your product outperforms the competition using a high-quality animation of the manufacturing process, the sale becomes a lot easier.
Pro Tip: Consider incorporating lattice structures into your design iterations to improve weight reduction and overall performance. When showcasing engineering breakthroughs in heat exchange technology, visualisation becomes essential. 3D animation enhances industrial equipment demonstrations, especially for heat exchangers that use advanced design possibilities, by making complex internal mechanics easy to understand.
Practical Tips for Implementing 3D Visualisation
If you are a UK-based engineering firm looking to bridge the gap between your AM designs and your clients, consider the available heat and design parameters that enhance performance.
-
Don’t Skimp on Detail: Precision is crucial in the manufacture of high-efficiency heat exchangers to avoid costly failures. Ensure your 3D models include the actual surface texture produced by the 3D printer, as this affects heat transfer in the compact heat exchanger.
-
Use Colour Coding: Implementing colour coding can help visualize flow paths in high-performance heat exchangers, thereby improving performance. In your visualisations, use clear gradients (blue for cold, red for hot) to make the data intuitive.
-
Integrate VR to enhance the design flexibility of your presentations and prototypes. If possible, use Virtual Reality to visualize the design flexibility offered by additively manufactured components. Allowing an engineer to “stand inside” a heat exchanger design provides a sense of scale that a computer screen cannot match, especially when considering complex geometries in high-temperature applications.
-
Keep it Clean: Avoid “visual clutter” in your animations. Focusing on the flow paths and the core thermal zones in heat exchangers may reveal new efficiencies.
The Future is Layered
As we look toward the future of UK manufacturing, the synergy between 3D printing and 3D visualisation in creating efficient heat exchangers will continue to grow, particularly with advances in additive manufacturing technologies. We are moving away from a world of “standard parts” and toward a world of “optimised parts.”
The additive manufacturing heat exchangers of tomorrow will be lighter, smaller, and more efficient than anything we’ve seen before, particularly in the aerospace industry. But to build them, we have to see them first. Visualisation is no longer a “nice-to-have” add-on; it is the lens through which we will design the next generation of industrial technology, particularly for the manufacture of heat exchangers.
Bring your heat exchanger designs to life with crystal-clear 3D visualisation. Explore how industrial and engineering 3D animations can make complex mechanics easy to understand. Discover more here.
FAQs: Why Additive Manufacturing Heat Exchangers Need 3D Visualisation
Why is 3D printing additive manufacturing?
3D printing is called additive manufacturing because it builds objects, like complex heat exchangers, by adding material layer by layer. This is the opposite of traditional “subtractive” manufacturing, where you start with a block of material and cut away what you don’t need, limiting the design freedom of additive manufacturing.
Can you 3D print a heat exchanger?
Yes, absolutely! It is becoming a common practice in aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors to utilize additive manufacturing for new heat exchanger designs. By 3D printing them, engineers can create complex internal geometries that improve heat transfer and reduce the overall weight of the 3D printed heat exchanger.
Why is additive manufacturing important for 3D printing in space?
In space, every gram of weight costs money to launch. Additive manufacturing allows astronauts to print spare parts on demand, reducing the need to carry heavy inventory and improving the efficiency of the manufacturing process.7 It also allows for the creation of highly optimized, lightweight structures that can be fabricated using advanced printing technology, producing heat exchangers that would be impossible to manufacture on Earth and transport.
What is the main advantage of additive manufacturing 3D printing in construction?
The main advantage is the ability to create complex, bespoke architectural shapes with significantly less waste, thanks to the design freedom of additive manufacturing. It also allows for faster build times on-site and the ability to use sustainable materials, such as local soil or recycled concrete, to create structural components for compact heat exchangers, reducing pressure drop.